Understanding and Preventing Sarcopenia: Key Tips to Maintain Muscle Mass
Sarcopenia, the age-related loss of muscle mass and strength, can…
Sarcopenia, the age-related loss of muscle mass and strength, can significantly affect your independence and quality of life. Understanding and preventing sarcopenia is crucial for staying active as you age. In this article, you’ll learn about sarcopenia’s causes, symptoms, and practical strategies to maintain your muscle health.
Key Takeaways
- Sarcopenia is a progressive loss of muscle mass and function affecting older adults, leading to decreased independence and increased care needs.
- Combatting sarcopenia requires a combination of resistance training, proper nutrition, and adequate protein intake; early intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
- Consulting healthcare providers for personalized strategies and regular monitoring of muscle health is crucial for effective management of sarcopenia.
Introduction to Sarcopenia
Sarcopenia is a natural part of the aging process, marked by the progressive loss of muscle mass, strength, and function. This decline in skeletal muscle mass can affect both men and women, often leading to noticeable changes in physical performance and daily abilities. While aging is the primary driver, factors such as physical inactivity, inadequate nutrition, and chronic diseases can accelerate muscle loss and make it more severe.
As muscle mass and strength decrease, everyday tasks can become more challenging, and the risk of falls and injuries rises. Fortunately, sarcopenia is not inevitable. Incorporating resistance training and maintaining proper nutrition are proven ways to help preserve muscle mass and strength as you age. By staying active and ensuring your body receives the nutrients it needs, you can slow the progressive loss of muscle and support your overall health and independence.
What is Sarcopenia?
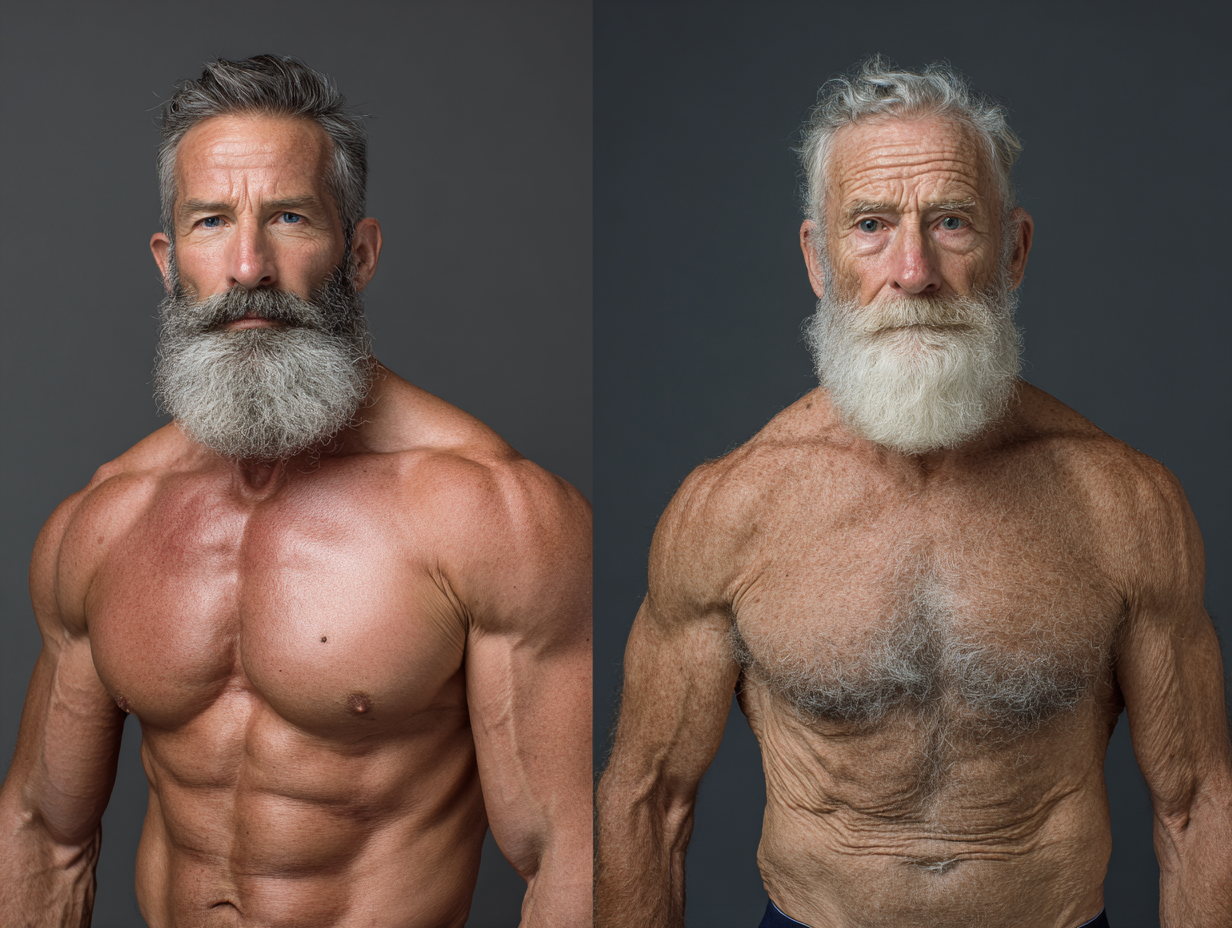

Sarcopenia might be an unfamiliar term, but it significantly impacts the elderly population, primarily through a gradual decline in muscle mass. This condition also involves a decrease in muscle function due to aging, predominantly affecting individuals aged 60 and older. Sarcopenia prevalence ranges from 5% to 13% in this age group, potentially affecting up to 50% of those aged 80 or older.
This condition does not discriminate; it affects both men and women equally. The impact of sarcopenia on an individual’s life can be profound, reducing their capacity to maintain independence and often necessitating long-term care. Sarcopenia impairs the ability to perform daily tasks, which can further diminish independence and increase the need for long-term care. Recognized as a specific disease by the CDC, sarcopenia now receives more attention in terms of diagnosis and management, making it a critical area of focus for healthcare providers and researchers.
Starting at age 30, muscle loss typically occurs at a rate of 3% to 5% per decade, accelerating with age and leading to a significant decrease in muscle fibers number and size, causing muscle thinning and loss of muscle mass. Understanding this process is crucial for developing effective strategies to combat sarcopenia and maintain muscle health as we age.
Recognizing the signs early and taking proactive steps can mitigate the effects of sarcopenia. This guide will provide you with the knowledge and tools needed to address this condition head-on, ensuring a better quality of life and prolonged independence.
Causes of Sarcopenia
The causes of sarcopenia are multifaceted, involving a combination of biological, lifestyle, and health factors. There are several risk factors that contribute to the development of sarcopenia, including inflammatory cytokines, a sedentary lifestyle, and vitamin D deficiency. As we age, our bodies undergo several changes that contribute to muscle loss. One of the primary biological factors is the reduced ability to produce protein necessary for muscle growth. This decline is often accompanied by hormonal changes and altered hormone levels, such as testosterone and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), both of which are linked to muscle loss. Reduced levels of anabolic hormones, including testosterone, IGF-1, and estrogens, play a crucial role in muscle protein synthesis and the regulation of muscle mass in aging populations.
Chronic diseases also play a significant role in the onset and progression of sarcopenia. Conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), diabetes, and cancer are associated with higher rates of muscle loss and various health complications. Insulin resistance, which is common in aging and metabolic disorders, impairs muscle protein synthesis and contributes to muscle loss in sarcopenia. These metabolic diseases can exacerbate the decline in muscle mass and function, making it crucial to manage them effectively to prevent further deterioration.
Malnutrition, particularly insufficient protein intake, is another critical factor contributing to sarcopenia. As we age, our dietary needs change, and failing to meet these needs can accelerate muscle mass loss. Ensuring inadequate nutrition is therefore essential for maintaining muscle health and preventing sarcopenia.
Additionally, the phenomenon of sarcopenic obesity, where individuals have both low muscle mass and high body fat, further complicates the situation. This condition, along with the loss of nerve cells that reduce signaling between the brain and muscles, adds to the complexity of sarcopenia and reduced muscle mass. Understanding these causes helps in developing comprehensive strategies to combat the condition effectively.
Addressing these underlying causes through lifestyle changes, proper nutrition, and medical management can significantly reduce the risk of sarcopenia and enhance muscle health.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Early recognition of sarcopenia symptoms can significantly improve management of the condition. Common symptoms include muscle weakness, decreased stamina, and difficulties in performing daily activities. These symptoms can manifest as difficulty climbing stairs, poor balance, and a noticeable decrease in muscle size.
Diagnose sarcopenia involves assessing both skeletal muscle mass and function. One of the methods used is bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), which estimates skeletal muscle by measuring the body’s electrical conductivity. This non-invasive technique provides valuable insights into the amount of muscle present in the body.
Ultrasound is another reliable tool for evaluating muscle quantity and quality. It allows healthcare providers to visualize the muscle tissue and assess its condition, making it an effective method for diagnosing sarcopenia. Combining these diagnostic tools with physical performance tests, such as grip strength and walking speed, provides a comprehensive assessment of muscle health.
Early diagnosis is crucial for implementing effective interventions that can slow down or even reverse the progression of sarcopenia. Understanding the symptoms and diagnostic methods enables individuals to proactively assess their muscle health and seek appropriate medical advice.
Effects of Sarcopenia
The effects of sarcopenia extend far beyond just muscle weakness—they can impact nearly every aspect of your health and daily life. Reduced muscle mass and strength can lead to decreased physical performance, making activities like walking, climbing stairs, or carrying groceries more difficult. This loss of muscle can also increase the risk of falls and fractures, which may result in a loss of independence and mobility.
Sarcopenia is also linked to a higher risk of chronic diseases, including metabolic diseases, kidney disease, and certain cancers. As muscle mass declines, it can negatively affect your body’s ability to regulate blood sugar, maintain a healthy weight, and support immune function. Early intervention is key: regular strength training, aerobic exercise, and balance exercises can help maintain muscle mass and strength, while a healthy diet with adequate protein intake supports muscle repair and growth.
By prioritizing physical activity and proper nutrition, you can help prevent sarcopenia and its associated health risks. If you notice signs of muscle weakness or reduced muscle mass, consult a healthcare provider to diagnose sarcopenia and develop a personalized plan to maintain your muscle health and overall well-being. Regular exercise and a balanced diet are essential steps toward healthy aging and preserving your independence.
Importance of Preventing Sarcopenia
Preventing sarcopenia maintains a high quality of life and independence as we age. Maintaining muscle mass keeps individuals strong, balanced, and capable of performing daily activities with ease. Resistance exercise and adequate protein intake help optimize body composition by increasing skeletal muscle mass and reducing body fat, which is crucial for healthy aging. It also has significant health benefits, including improved heart health, better blood sugar control, and increased longevity.
Low muscle function significantly elevates the risk of losing physical independence, emphasizing the need to focus on muscle quality. Sarcopenia can lead to difficulties in performing everyday tasks, such as climbing stairs and maintaining balance, which can severely impact an individual’s ability to live independently.
Early intervention from healthcare professionals is vital for managing sarcopenia before it significantly impacts daily activities. Healthy lifestyle changes, such as regular physical activity and proper nutrition, significantly enhance muscle health and combat sarcopenia.
Adequate hydration is also critical for muscle function and recovery, directly influencing overall muscle health. Dehydration can lead to decreased muscle performance and an increased risk of injury, emphasizing the importance of staying hydrated. Supplements like vitamin D can further enhance muscle strength and health, providing additional support in the fight against sarcopenia.
Understanding the importance of preventing sarcopenia and taking proactive steps allows individuals to enjoy a healthier, more active life well into their later years.
Effective Strategies to Combat Sarcopenia

Combatting sarcopenia involves a multifaceted approach that includes regular physical activity, proper nutrition, and adequate protein intake. These strategies work together to maintain muscle mass and strength, making them essential components of any sarcopenia prevention plan.
Resistance training is one of the most effective ways to prevent sarcopenia. When combined with proper nutrition, resistance training is essential to build muscle and maintain strength as you age. This form of exercise not only helps in building muscle but also enhances muscle strength and physical performance. Regular exercise combined with adequate protein intake forms a powerful strategy to combat sarcopenia.
Proper nutrition is crucial for maintaining muscle health. A diet high in protein and essential nutrients supports muscle growth and prevents age-related muscle loss. Tracking dietary habits and consulting healthcare providers for personalized recommendations can significantly enhance muscle health.
Incorporating these strategies into daily routines allows individuals to effectively combat sarcopenia and enjoy a stronger, healthier life.
Resistance Training
Resistance training is a cornerstone in the fight against sarcopenia, involving exercises that make your muscles work against a force, such as lifting weights or using resistance bands. This type of training is proven to help prevent sarcopenia by enhancing muscle strength and mass.
For effectiveness, resistance training should be performed at least twice a week. Strength training exercises targeting major muscle groups, such as the legs, back, and arms, are critical for maintaining muscle mass and strength in older adults. These strength exercises can include:
- Squats
- Lunges
- Push-ups
- Rows
- Upper body exercises such as chest presses or shoulder raises, which help strengthen the chest, shoulders, and back muscles
These exercises can be adjusted to match an individual’s fitness level.
A physical therapist can help develop a tailored exercise program aimed at combating sarcopenia. A professional can provide guidance on proper form, progression, and intensity, ensuring that the exercises are both safe and effective.
Incorporating resistance training into your routine not only helps in building muscle but also improves balance, coordination, and overall physical function. This multi-faceted approach makes resistance training an essential strategy for anyone looking to prevent or manage sarcopenia.
Proper Nutrition
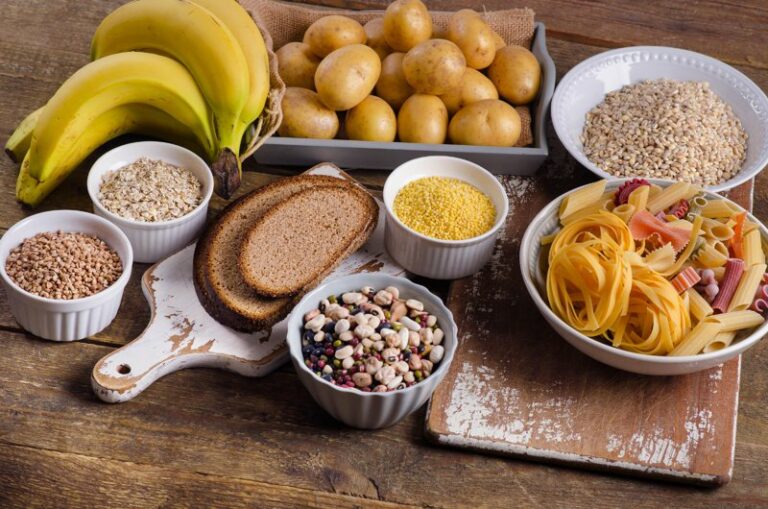
Proper nutrition is vital for maintaining muscle mass and preventing sarcopenia. A balanced diet rich in protein and essential nutrients supports muscle growth and overall health. High-quality protein sources provide essential amino acids, which are critical for muscle protein synthesis and maintaining muscle health in older adults. Older adults, in particular, need to focus on dietary habits to ensure they consume adequate protein and vital nutrients.
Incorporating diverse protein sources can significantly enhance muscle health and combat age-related muscle loss. These sources include:
- Lean meats
- Dairy
- Beans
- Nuts
Adequate protein intake helps preserve lean body mass and supports the development of lean muscle mass, both of which are important for functional independence.
Tracking dietary habits helps ensure nutritional needs are met, which is crucial for optimal nutrition, muscle maintenance, and a healthy diet. Meeting protein needs is especially important for older adults, and recommendations may exceed the standard RDA to support muscle maintenance.
Healthcare providers can offer personalized dietary recommendations to enhance muscle health and effectively address sarcopenia. Consulting a primary care provider can also assist in determining the appropriate nutritional supplements to support muscle maintenance.
By focusing on proper nutrition, you can provide your body with the essential building blocks it needs to maintain muscle mass and prevent sarcopenia.
Additional Lifestyle Changes to Support Muscle Health
Several lifestyle changes beyond resistance training and proper nutrition can support muscle health and prevent sarcopenia. Physical inactivity and obesity accelerate sarcopenia development, making it crucial to stay active and maintain a healthy weight. Individuals who are physically inactive are at greater risk for muscle mass loss and age-related muscle decline.
Regular physical activity combined with a high-protein diet is essential for preventing muscle mass loss associated with aging. Incorporating diverse physical activities enhances overall muscle health and function. It is recommended that older adults consume higher protein amounts per meal to effectively stimulate muscle protein synthesis.
Each main meal should contain:
- Approximately 0.6 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight.
- At least 5-6 grams of leucine when consuming three protein meals daily, which can significantly enhance muscle health.
- A variety of protein sources to further improve the amino acid profile that benefits older adults, ensuring enough protein for optimal health.
These additional lifestyle changes support muscle health and reduce the risk of sarcopenia.
Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining muscle mass and overall health, especially in older adults. Activities like:
- walking
- swimming
- balance exercises significantly improve muscle strength and coordination. These exercises not only help in maintaining muscle mass but also enhance physical performance and functional ability.
A routine that includes regular exercise fosters consistency and improves muscle health outcomes. Technology, such as fitness trackers, can aid in monitoring physical activity levels and progress, making it easier to stay motivated and on track.
Aerobic exercise combined with balance exercises provides a comprehensive approach to improving muscle health. These activities enhance cardiovascular health, improve endurance, and support muscle function, making them essential components of a well-rounded exercise regimen.
Remaining physically active and incorporating diverse exercises into your routine can prevent muscle atrophy and support long-term health. Staying active helps maintain independence and enjoy a higher quality of life.
Reducing Sedentary Behaviour
Sedentary behaviour, such as prolonged sitting, can have detrimental effects on muscle health. Reducing sedentary time improves strength and overall function in older adults, emphasizing the importance of active breaks throughout the day. Minimizing extended periods of inactivity improves muscle strength and overall health.
Incorporating brief movement breaks into your daily routine significantly improves muscle health. For instance, standing up and stretching every hour, taking short walks, or performing light exercises can counteract prolonged sitting’s negative effects.
Limiting prolonged sitting and incorporating active breaks leads to better muscle health and lowers the risk of age-related muscle loss. Encouraging a more active lifestyle helps maintain muscle mass and functional ability, making it essential for preventing sarcopenia.
Reducing sedentary behaviour and staying active improves overall health, enhances muscle strength, and prevents sarcopenia progression.
Hydration and Supplements
Proper hydration supports muscle recovery and enhances nutrient delivery to muscle cells, making it crucial for muscle health. Adequate protein and nutrient intake also supports the immune system, helping regulate immune responses and muscle repair. Staying adequately hydrated can improve muscle function and reduce the risk of injury, making it an essential component of overall health.
Vitamin D plays a role in muscle function and strength, making it important for muscle health. Vitamin D supplementation enhances muscle strength, particularly in individuals with low baseline levels. Aging-related changes in gut microbiota can affect carbohydrate metabolism, which in turn impacts energy production, amino acid synthesis, and overall muscle health. Including vitamin D in your daily routine supports muscle health and prevents sarcopenia.
Supplements and their benefits include:
- Fish oil: reduces inflammation and supports muscle mass maintenance.
- Creatine: supports muscle mass gains and improves exercise performance in older adults.
- Vitamin D and creatine: assist in maintaining muscle mass and promoting strength.
Ensuring proper hydration and incorporating beneficial supplements into your diet supports muscle health and reduces the risk of sarcopenia.
Monitoring Progress and Adjustments
Monitoring progress in combating sarcopenia is essential for making informed adjustments to exercise and nutrition plans. Regularly measuring muscle strength and mass helps track progress and identify areas needing improvement. Physical performance tests, such as walking speed or grip strength, provide insight into muscle health.
Adjustments to exercise routines based on individual progress and feedback optimize strength training effectiveness. Consulting healthcare providers helps monitor muscle health and adjust treatment plans based on individual progress and needs.
Regularly monitoring progress and making necessary adjustments effectively combats sarcopenia and maintains muscle health.
Consulting Healthcare Providers
Consulting healthcare providers helps understand personalized strategies to prevent and manage sarcopenia. Individuals with chronic conditions should consult their doctor before starting strength training to ensure the exercises are safe and appropriate.
Personalized strategies from healthcare providers lead to more effective sarcopenia management and better health outcomes. Healthcare providers offer guidance on proper exercise techniques, nutrition plans, and supplement recommendations tailored to specific needs.
Consulting a healthcare provider helps develop a comprehensive plan to prevent and manage sarcopenia, ensuring better muscle health and overall well-being.
Summary
In conclusion, sarcopenia is a significant concern for older adults, but it is preventable and manageable with the right strategies and lifestyle changes. Maintaining muscle mass is crucial for staying strong, balanced, and independent. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and effective strategies to combat sarcopenia, you can take proactive steps to ensure better muscle health and overall well-being.
Incorporating resistance training, proper nutrition, and adequate protein intake into your daily routine can significantly enhance muscle health and prevent sarcopenia. Additionally, making other lifestyle changes, such as regular physical activity, reducing sedentary behaviour, and ensuring proper hydration and supplementation, can further support muscle health.
Monitoring your progress and consulting with healthcare providers can help you develop personalized strategies to prevent and manage sarcopenia effectively. By taking these steps, you can enjoy a healthier, more active life well into your later years.
Remember, it’s never too late to take control of your muscle health. Start today and make the changes necessary to stay strong, healthy, and vibrant.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sarcopenia?
Sarcopenia is the gradual loss of muscle mass and function that typically affects those over 60, but you can combat it! Staying active and incorporating strength training into your routine can help maintain your independence and vitality as you age.
What are the main causes of sarcopenia?
Sarcopenia primarily arises from the natural aging process, chronic diseases, malnutrition, and reduced nerve signalling to muscles. Taking proactive steps in diet and exercise can help combat this condition and maintain your strength as you age!
How can I prevent sarcopenia?
To prevent sarcopenia, focus on regular resistance training and a balanced diet high in protein and essential nutrients. Staying active and hydrating properly will also empower you to maintain muscle health!
What are the common symptoms of sarcopenia?
If you’re noticing muscle weakness, decreased stamina, or struggles with daily activities, these could be signs of sarcopenia. Take these symptoms seriously and consider consulting a healthcare professional for support!
How is sarcopenia diagnosed?
Sarcopenia is diagnosed through assessments of muscle mass and function using methods like bioelectrical impedance analysis, ultrasound, and physical performance tests such as grip strength and walking speed. Recognizing these indicators early can empower you to take action and preserve your muscle health!